Gin 源码分析 - 路由
Gin 源码分析概览 中提到了 Gin 框架的路由树是通过 基数树 实现的,它是怎么一种数据结构以及是如何做到高性能的呢?另外很多地方提到了 Gin 路由是基于 HttpRouter,但为啥 go.mod 中没有这个依赖呢?本文将为你解答这些疑问。
前缀树和基数树
首先我们来看下两种数据结构,它们在自动补全、拼写检查、路由匹配上应用非常广泛。
前缀树(Trie) 是一种树形数据结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串数据集中的键。想进一步了解前缀树的实现,可以参考:LeetCode - 208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
而 基数树(Radix Trie) 是一种压缩的前缀树,它合并了公共的路径,减少了存储空间。下面分别是两种树的结构图:
| 前缀树 | 基数树 |
|---|---|
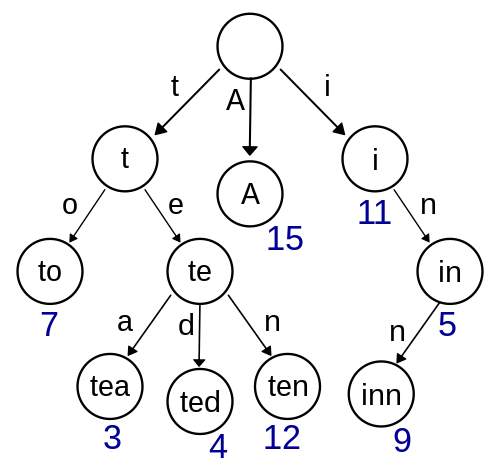 | 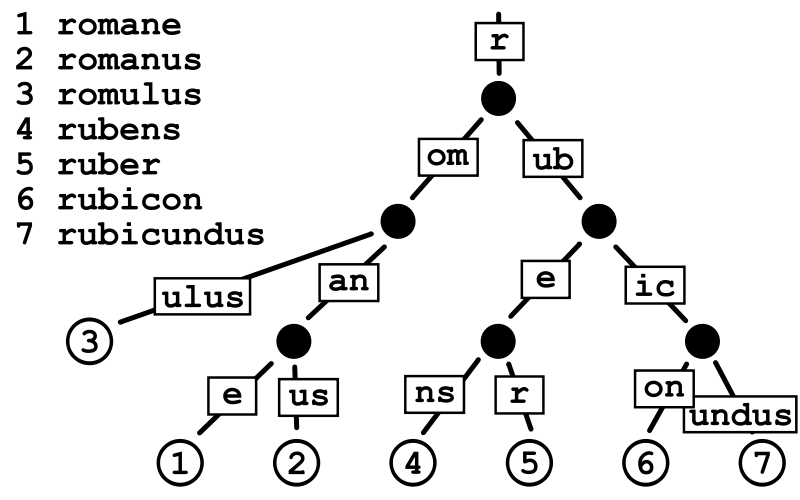 |
基数树相比前缀树节省了大量前缀存储空间,且同样在存储和查找上能做到 O(strlen),另外还支持完全匹配、前缀匹配、前驱查找、后继查找等高级查找方式。
Gin 路由树的定义
Gin 路由树的实现虽然基于 HttpRouter 库,但是源码中自己实现了算法逻辑,算法代码文件为:tree.go, 因此 go.mod 中不需要依赖 HttpRouter。
我们先回顾一下,第一次看到路由树是在 Engine.New 方法中,New 中为 Engine 对象初始化了一个 trees 数组属性,其中结构体为 methodTrees:
// https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/v1.9.1/gin.go#L183
func New() *Engine {
// ...
engine := &Engine{
// ...
trees: make(methodTrees, 0, 9),
}
// ...
}// https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/v1.9.1/tree.go#L57
type methodTrees []methodTree
// https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/v1.9.1/tree.go#L52
type methodTree struct {
method string
root *node
}
// https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/v1.9.1/tree.go#L116
type node struct {
path string
indices string
wildChild bool
nType nodeType
priority uint32
children []*node // child nodes, at most 1 :param style node at the end of the array
handlers HandlersChain
fullPath string
}首先我们看到 Engine 对象中会存储一个长度为 0 容量为 9 的 methodTree 数组。这个 methodTree 就是基数树,容量为 9 是因为 HTTP 方法最多 9 个。举个例子如果我们的应用只注册了 GET、POST 两种 HTTP 方法的路由,那么应用的 methodTree 数组最终长度就是 2。
对于 methodTrees 底层数据结构,我们第一反应会想到使用 map,但这里 Gin 选用了数组。主要原因这里的数组长度小且有限(最多 9),搜索成本不高,但能节省内存。思维拓展一下,这也告诉了我们,选择数据结构应该是结合场景和数据量一起考虑。
其他关键信息都在 node 结构体了:
path: 路径段。比如依次插入了路径 /romane 和 /romanus ,那么会产生一个父节点,它的 path 为 /romanindices: 是一个字符串,节点的所有子节点的首字母。比如上面例子中,父节点的 indices 为 "eu"nType: 是一个枚举类型 nodeType,表示该节点的类型,取值有:- root:根节点
- param:参数节点,比如 :id
- catchAll:* 开头的节点,比如 *name
- static:静态节点,除上述以外的节点
children:*node类型的切片,表示该节点的所有子节点。
Gin 路由树的构建
路由树的构建发生在 “注册路由” 过程中:
// https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/v1.9.1/gin.go
func (engine *Engine) addRoute(method, path string, handlers HandlersChain) {
// ...
root := engine.trees.get(method)
if root == nil {
root = new(node)
root.fullPath = "/"
engine.trees = append(engine.trees, methodTree{method: method, root: root})
}
// 在 HTTP 方法对应的基数树中添加路由节点,节点中记录路由路径和所有处理程序
root.addRoute(path, handlers)
// ...
}// https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/v1.9.1/tree.go#L152-L266
func (n *node) addRoute(path string, handlers HandlersChain) {
fullPath := path
n.priority++
// 空树直接插入当前节点
if len(n.path) == 0 && len(n.children) == 0 {
n.insertChild(path, fullPath, handlers)
n.nType = root
return
}
parentFullPathIndex := 0
walk:
for {
// 找到新路径和当前节点路径的最长公共字串长度
// 比如新路径为 /romanus,当前节点路径为 /romane,则 i 等于 5
i := longestCommonPrefix(path, n.path)
// 根据上面的例子,5 < len("romane"),需要进行当前节点的拆分处理
// 即拆分当前节点为 "roman" -> "e"
if i < len(n.path) {
// ...
}
// 根据上面的例子,5 < len("romanus"),需要递归 walk 代码块来处理不匹配的字串 "us"
// 递归过程就是为不匹配的字串创建新节点。实际逻辑比较复杂,这里不详细展开
if i < len(path) {
// ...
}
// ...
}
}Gin 路由树的搜索
路由树的搜索发生在 “处理请求” 里:
// https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/v1.9.1/gin.go#L592
func (engine *Engine) handleHTTPRequest(c *Context) {
// ...
t := engine.trees
for i, tl := 0, len(t); i < tl; i++ {
// 找到对应 HTTP 方法的路由树
if t[i].method != httpMethod {
continue
}
root := t[i].root
// 在路由树中搜索匹配的路由节点
value := root.getValue(rPath, c.params, c.skippedNodes, unescape)
if value.params != nil {
c.Params = *value.params
}
if value.handlers != nil {
c.handlers = value.handlers
c.fullPath = value.fullPath
c.Next()
c.writermem.WriteHeaderNow()
return
}
// ...
}
// ...// https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/v1.9.1/tree.go#L420
func (n *node) getValue(path string, params *Params, skippedNodes *[]skippedNode, unescape bool) (value nodeValue) {
var globalParamsCount int16
walk: // Outer loop for walking the tree
for {
// 从根节点开始,逐级遍历路由树。
// 对于每个节点,根据节点的类型(root、param、catchAll、static)执行不同的匹配逻辑。
// 如果节点是 root 类型,则匹配根路径。
// 如果节点是 param 类型,则匹配参数。
// 如果节点是 catchAll 类型,则匹配通配符。
// 如果节点是 static 类型,则简单比较字符串。
// ...
}
}搜索路由树的逻辑主要在 node.getValue 方法里,代码注释中给了大致步骤。
我们这里主要是滤清调用栈和数据结构,具体算法细节有兴趣的可以深入方法查看。
总结
本文先介绍了 Gin 框架的路由树的数据结构基数树,并深入 Gin 路由树的定义、构建和搜索源码,了解了一下 Gin 中路由树的具体实现。
其中核心算法的实现在文件 tree.go 中。
正是由于基数树数据结构低内存高性能的特点,使得 Gin 能拥有高效的路由解析功能。